1 Session 1: Introduction to the Arctic Data Center
1.1 Introduction to the Arctic Data Center and NSF Standards and Policies
1.1.1 Learning Objectives
In this lesson, you will learn:
- About the mission and structure of the Arctic Data Center
- How the Arctic Data Center supports the research community
- About data policies from the NSF Arctic program
1.1.2 Arctic Data Center - History and Introduction
The Arctic Data Center is the primary data and software repository for the Arctic section of National Science Foundation’s Office of Polar Programs (NSF OPP).
We’re best known in the research community as a data archive – researchers upload their data to preserve it for the future and make it available for re-use. This isn’t the end of that data’s life, though. These data can then be downloaded for different analyses or synthesis projects. In addition to being a data discovery portal, we also offer top-notch tools, support services, and training opportunities. We also provide data rescue services.
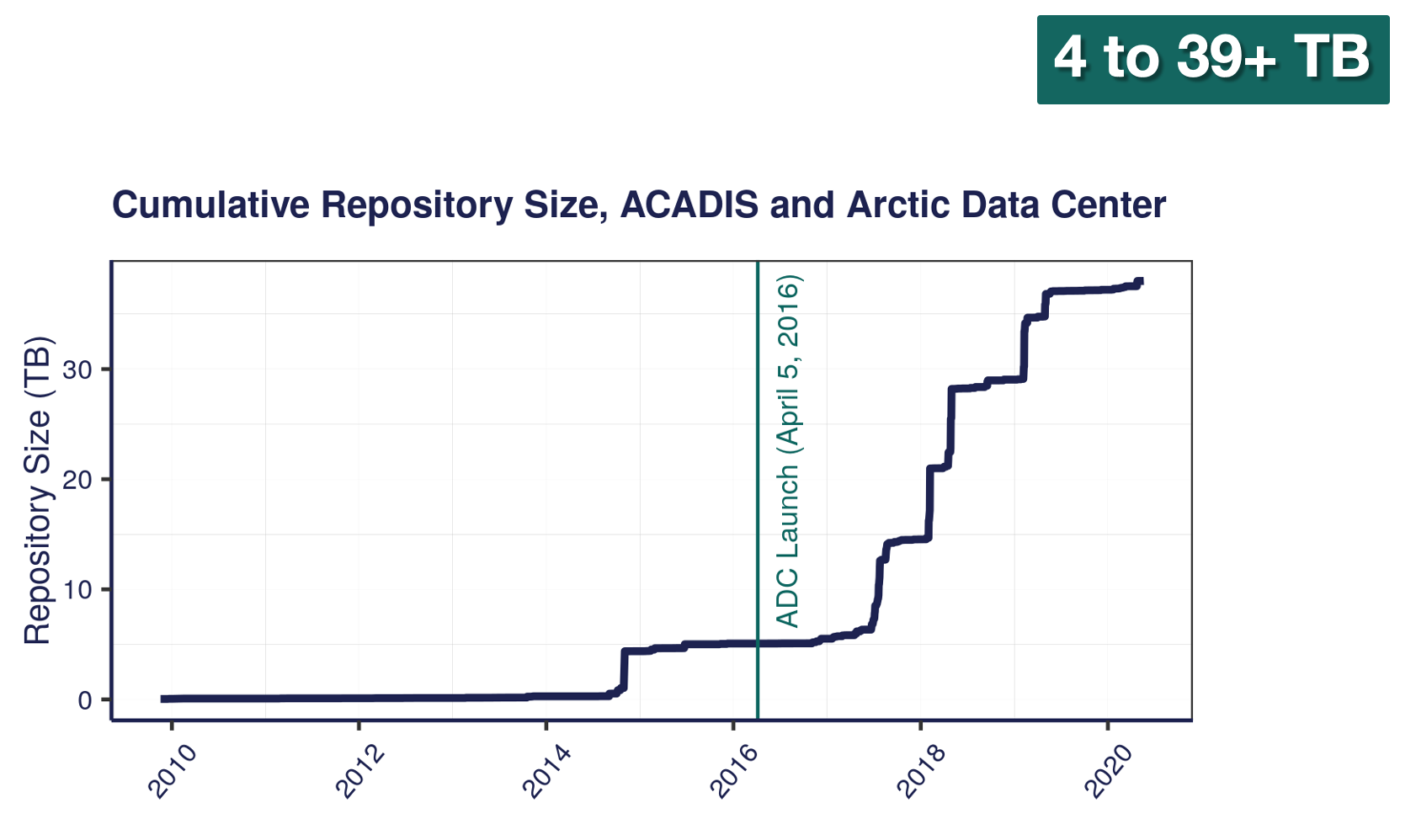
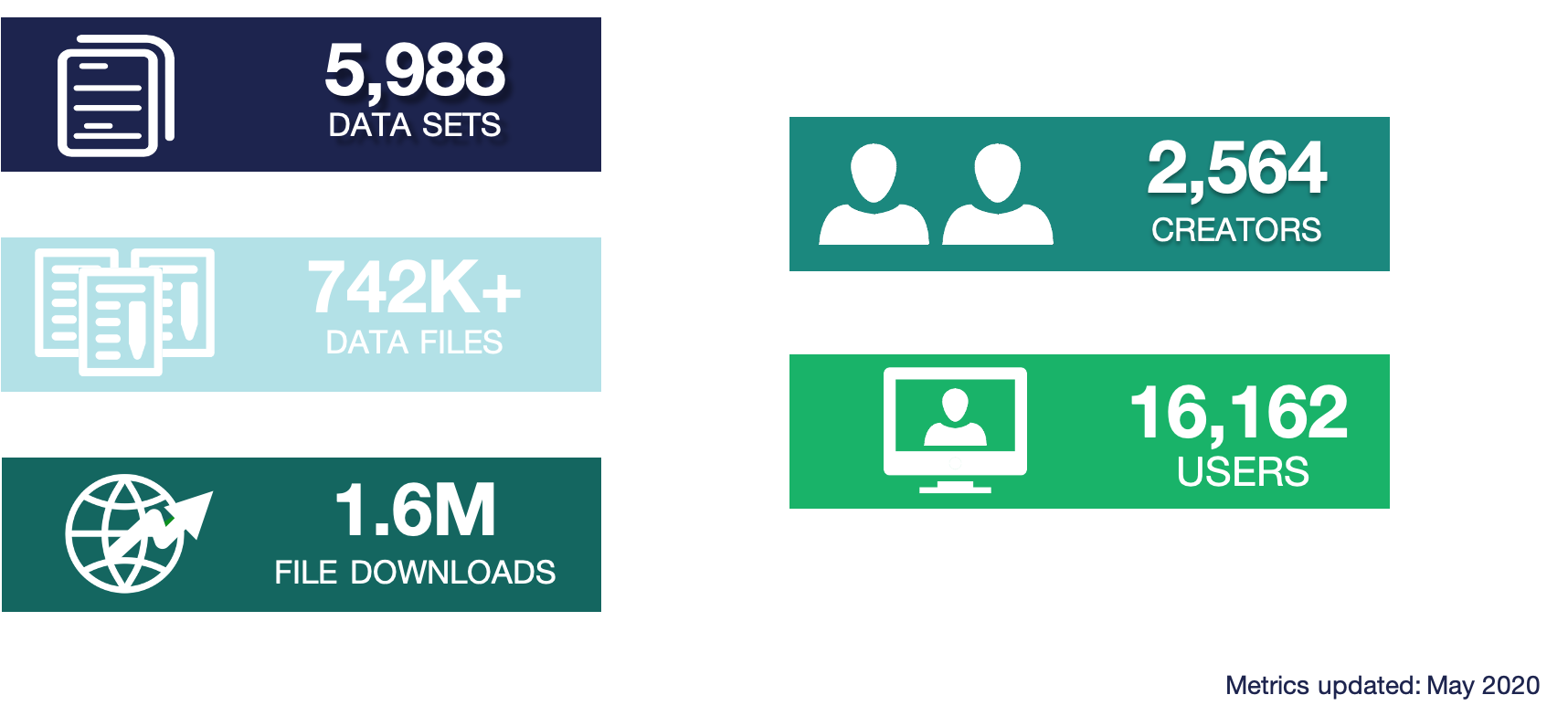
NSF has long had a commitment to data reuse and sharing. Since our start in 2016, we’ve grown substantially – from that original 4 TB of data from ACADIS to now over 39 TB. In the last year alone, we’ve seen a 16% growth in dataset count, and about a 30% growth in data volume. This increase has come from advances in tools – both ours and of the scientific community, plus active community outreach and a strong culture of data preservation from NSF and from researchers. We plan to add more storage capacity in the coming months, as researchers are coming to us with datasets in the terabytes, and we’re excited to preserve these research products in our archive. We’re projecting our growth to be around several hundred TB this year, which has a big impact on processing time. Give us a heads up if you’re planning on having larger submissions so that we can work with you and be prepared for a large influx of data.
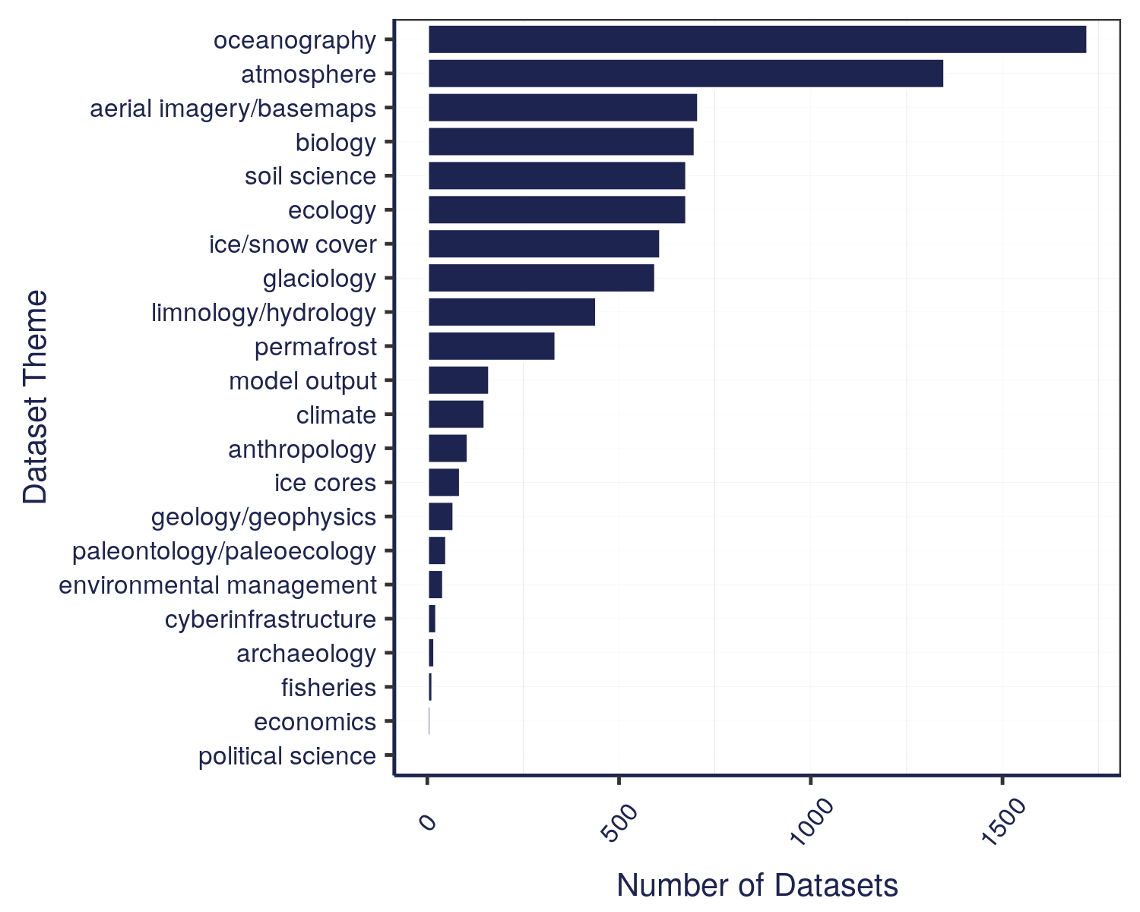
The data that we have in the Arctic Data Center comes from a wide variety of disciplines. These different programs within NSF all have different focuses – the Arctic Observing Network supports scientific and community-based observations of biodiversity, ecosystems, human societies, land, ice, marine and freshwater systems, and the atmosphere as well as their social, natural, and/or physical environments, so that encompasses a lot right there in just that one program. We’re also working on a way right now to classify the datasets by discipline, so keep an eye out for that coming soon.
Along with that diversity of disciplines comes a diversity of file types. The most common file type we have are image files in four different file types. Probably less than 200-300 of the datasets have the majority of those images – we have some large datasets that have image and/or audio files from drones. Most of those 5800+ datasets are tabular datasets. There’s a large diversity of data files, though, whether you want to look at remote sensing images, listen to passive acoustic audio files, or run applications – or something else entirely. We also cover a long period of time, at least by human standards. The data represented in our repository spans across centuries.
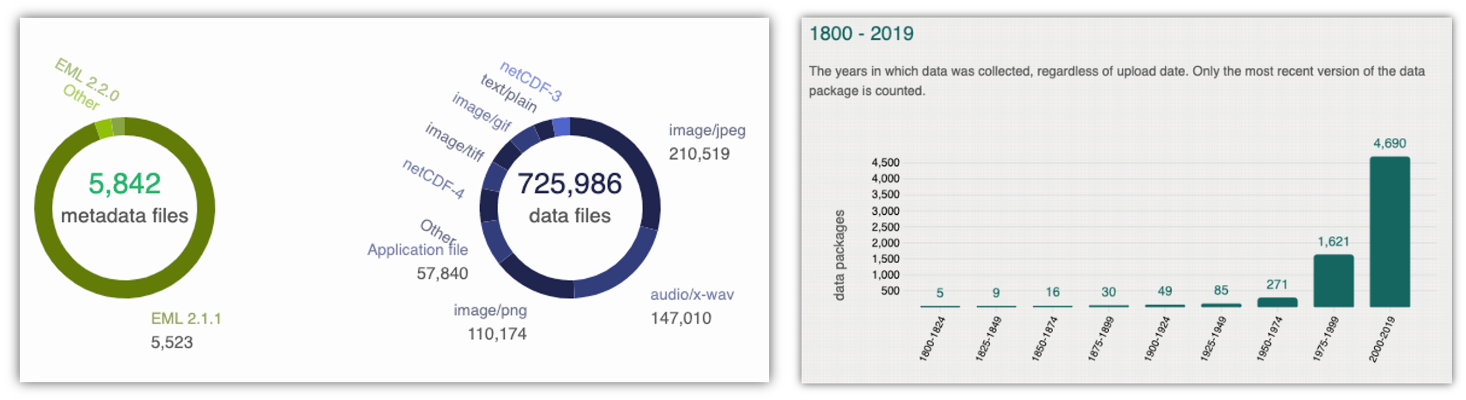
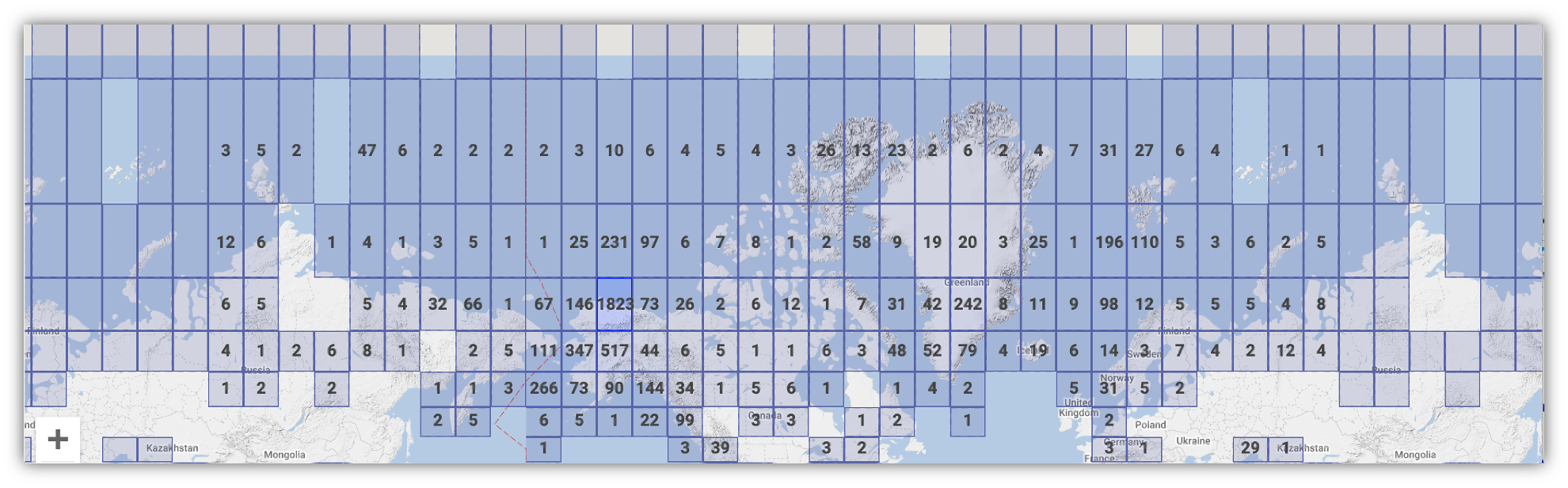
We also have data that spans the entire Arctic, as well as the sub-Arctic, regions.
1.1.3 Data Discovery Portal
To browse the data catalog, navigate to arcticdata.io. Go to the top of the page and under data, go to search. Right now, you’re looking at the whole catalog. You can narrow your search down by the map area, a general search, or searching by an attribute.
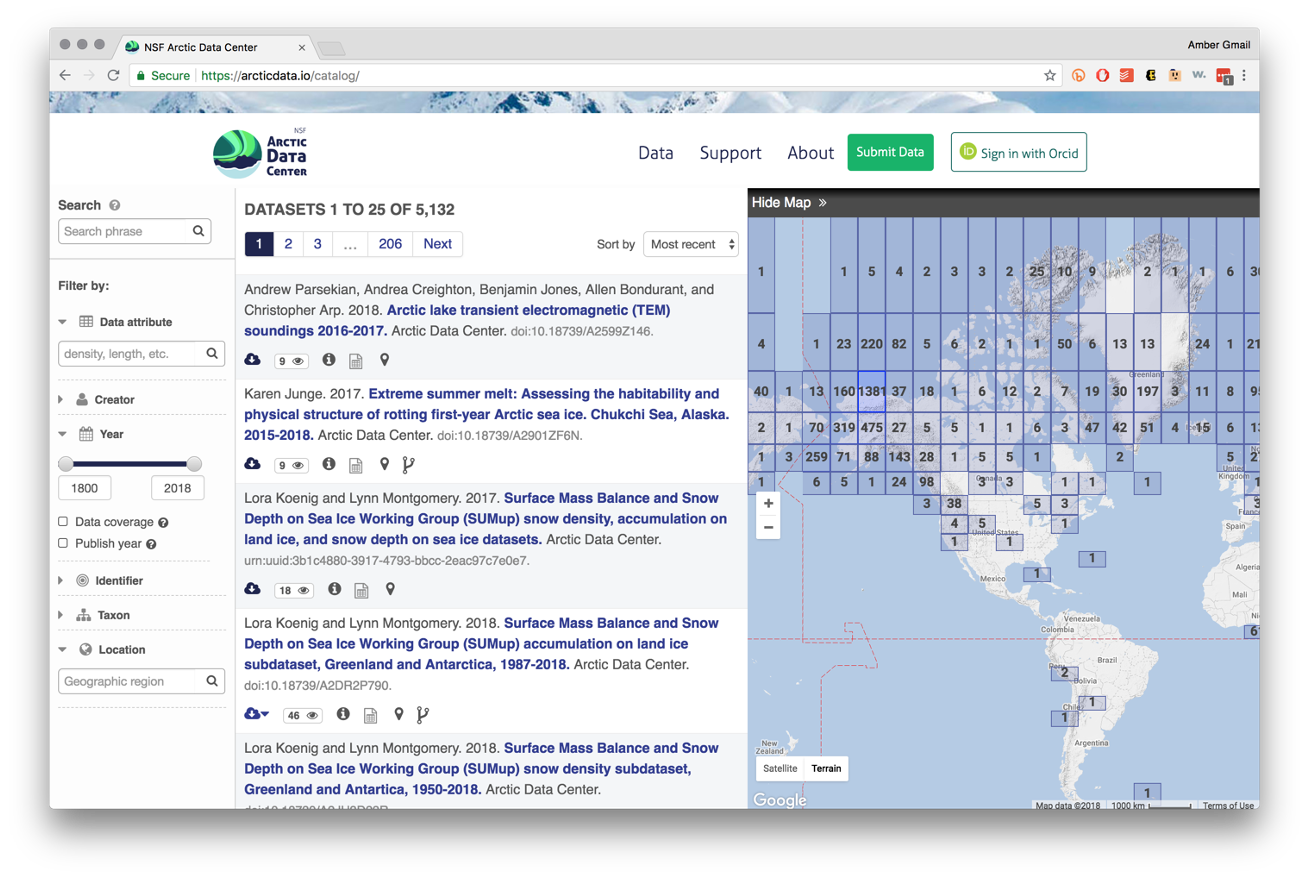 Clicking on a dataset brings you to this page. You have the option to download all the files by clicking the green “Download All” button, which will zip together all the files in the dataset to your Downloads folder. You can also pick and choose to download just specific files.
Clicking on a dataset brings you to this page. You have the option to download all the files by clicking the green “Download All” button, which will zip together all the files in the dataset to your Downloads folder. You can also pick and choose to download just specific files.
All the raw data is in open formats to make it easily accessible and compliant with FAIR principles – for example, tabular documents are in .csv (comma separated values) rather than Excel documents.
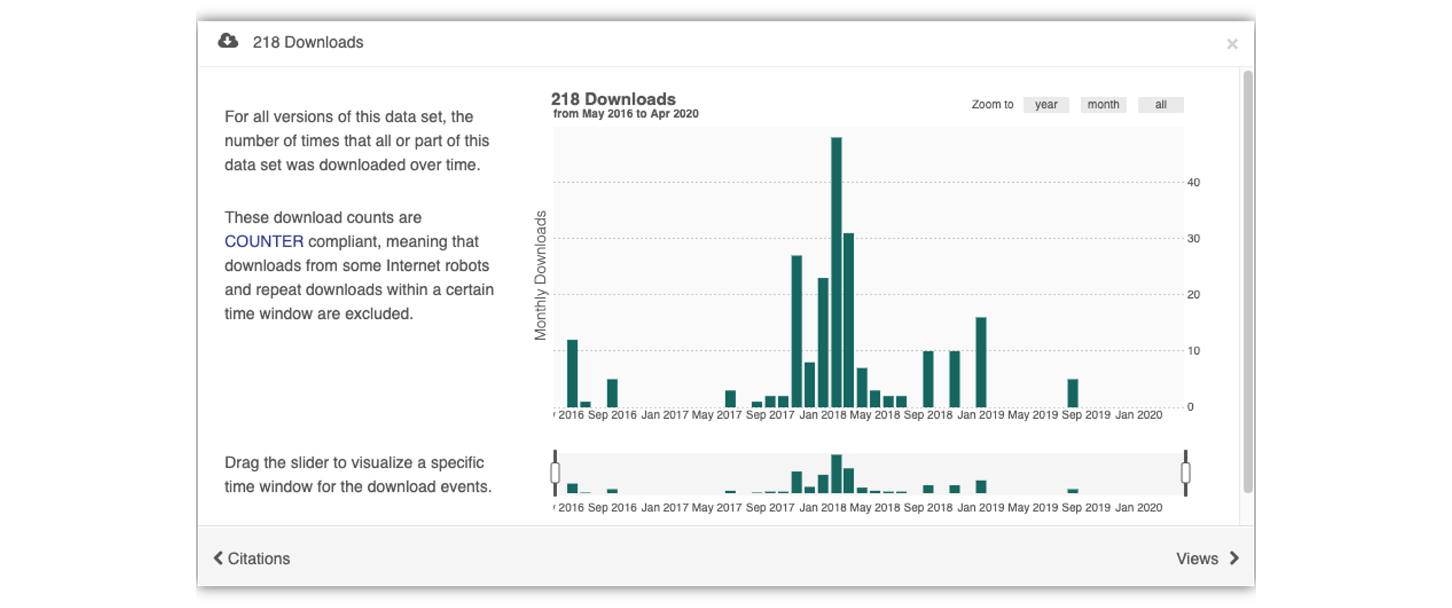
The metrics at the top give info about the number of citations with this data, the number of downloads, and the number of views. This is what it looks like when you click on the Downloads tab for more information.
Scroll down for more info about the dataset – abstract, keywords. Then you’ll see more info about the data itself. This shows the data with a description, as well as info about the attributes (or variables or parameters) that were measured. The green check mark indicates that those attributes have been annotated, which means the measurements have a precise definition to them. Scrolling further, we also see who collected the data, where they collected it, and when they collected it, as well as any funding information like a grant number. For biological data, there is the option to add taxa.
1.1.4 Tools and Infrastructure
We have a number of tools available to submitters and researchers who are there to download data. We also partner with other organizations, like Make Data Count and DataONE, and leverage those partnerships to create a better data experience.

One of those tools is provenance tracking. With provenance tracking, users of the Arctic Data Center can see exactly what datasets led to what product, using the particular script that the researcher ran.
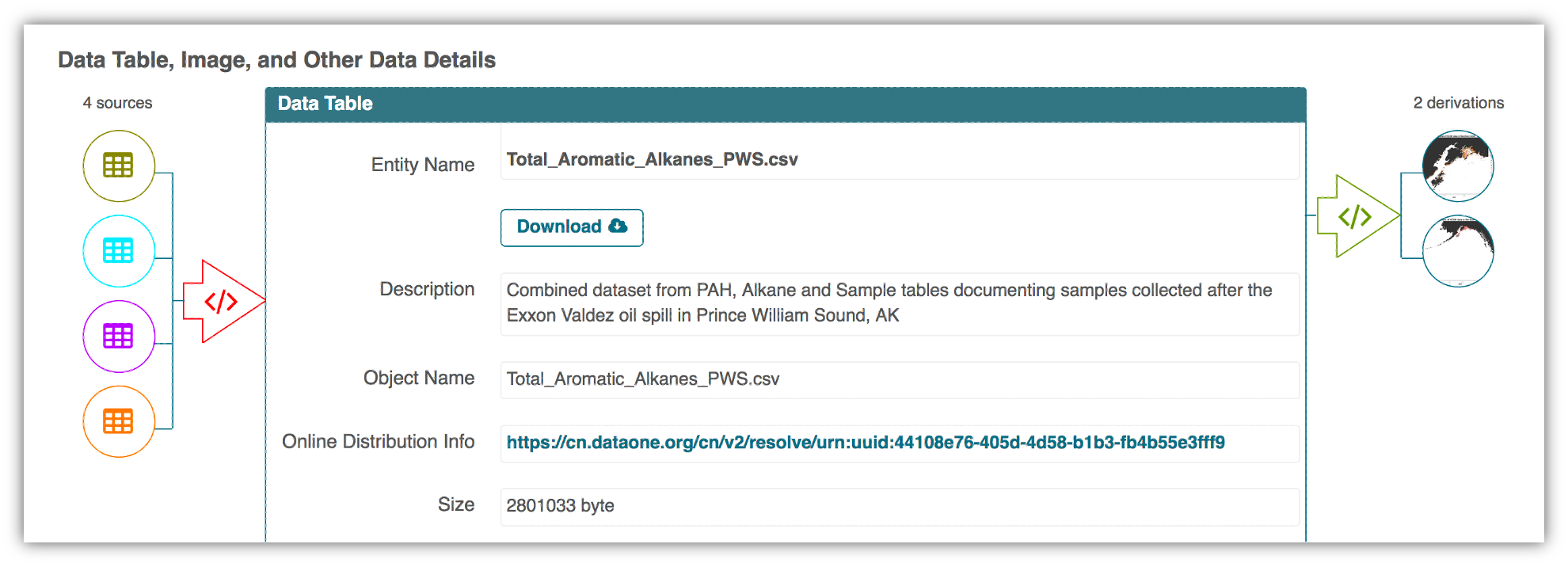
Another tool are our Metadata Quality Checks. We know that data quality is important for researchers to find datasets and to have trust in them to use them for another analysis. For every submitted dataset, the metadata is run through a quality check to increase the completeness of submitted metadata records. These checks are seen by the submitter as well as are available to those that view the data, which helps to increase knowledge of how complete their metadata is before submission. That way, the metadata that is uploaded to the Arctic Data Center is as complete as possible, and close to following the guideline of being understandable to any reasonable scientist.
1.1.5 Support Services
Metadata quality checks are the automatic way that we ensure quality of data in the repository, but the real quality and curation support is done by our curation team. The process by which data gets into the Arctic Data Center is iterative, meaning that our team works with the submitter to ensure good quality and completeness of data. When a submitter submits data, our team gets a notification and beings to evaluate the data for upload. They then go in and format it for input into the catalog, communicating back and forth with the researcher if anything is incomplete or not communicated well. This process can take anywhere from a few days or a few weeks, depending on the size of the dataset and how quickly the researcher gets back to us. Once that process has been completed, the dataset is published with a DOI (digital object identifier).
1.1.6 Training and Outreach
In addition to the tools and support services, we also interact with the community via trainings like this one and outreach events. We run workshops at conferences like the Ecological Society of America and the American Geophysical Union. We also run an intern and fellows program, and webinars with different organizations. We’re invested in helping to train the Arctic science community in reproducible techniques, since it facilitates a more open culture of data sharing and reuse.

We also strive to keep our fingers on the pulse of what researchers like yourselves are looking for in terms of support. We’re active on Twitter to share Arctic updates, data science updates, and specifically Arctic Data Center updates, but we’re also happy to feature new papers or successes that you all have had with working with the data. We can also take data science questions if you’re running into those in the course of your research, or how to make a quality data management plan. Follow us on Twitter and interact with us – we love to be involved in your research as it’s happening as well as after it’s completed.
Furthermore, we have a robust Data Fellows program to train early career researchers or recently graduated students in data science.
1.1.7 Data Rescue
We also run data rescue operations. We digitiazed Autin Post’s collection of glacier photos that were taken from 1964 to 1997. There were 100,000+ files and almost 5 TB of data to ingest, and we reconstructed flight paths, digitized the images of his notes, and documented image metadata, including the camera specifications.

1.1.8 Who Must Submit
Projects that have to submit their data include all Arctic Research Opportunities through the NSF Office of Polar Programs. That data has to be uploaded within two years of collection. The Arctic Observing Network has a shorter timeline – their data products must be uploaded within 6 months of collection.

Additionally, we have social science data, though that data often has special exceptions due to sensitive human subjects data. At the very least, the metadata has to be deposited with us.

1.1.9 Summary
All the above informtion can be found on our website or if you need help, ask our support team at support@arcticdata.io or tweet us @arcticdatactr!
Download slides: Arctic Data Center Overview and NSF Policies
1.2 Writing Good Data Management Plans
1.2.1 Learning Objectives
In this lesson, you will learn:
- Why create data management plans
- The major components of data management plans
- Tools that can help create a data management plan
- Features and functionality of the DMPTool
1.2.2 When to Plan: The Data Life Cycle
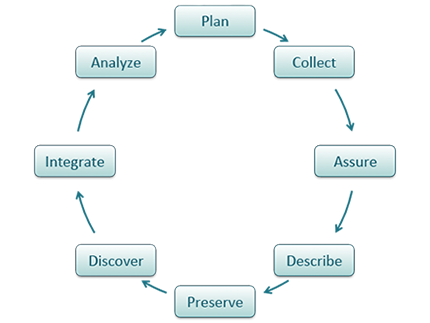
Shown below is one version of the Data Life Cycle that was developed by DataONE. The data life cycle provides a high level overview of the stages involved in successful management and preservation of data for use and reuse. Multiple versions of a data life cycle exist with differences attributable to variation in practices across domains or communities. It is not neccesary for researchers to move through the data life cycle in a cylical fashion and some research activities might use only part of the life cycle. For instance, a project involving meta-analysis might focus on the Discover, Integrate, and Analyze steps, while a project focused on primary data collection and analysis might bypass the Discover and Integrate steps. However, ‘Plan’ is at the top of the data life cycle as it is advisable to initiate your data management planning at the beginning of your research process, before any data has been collected.
1.2.3 Why Plan?
Planning data management in advance povides a number of benefits to the researcher.
- Saves time and increases efficiency; Data management planning requires that a researcher think about data handling in advance of data collection, potentially raising any challenges before they are encountered.
- Engages your team; Being able to plan effectively will require conversation with multiple parties, engaging project participants from the outset.
- Allows you to stay organized; It will be easier to organize your data for analysis and reuse.
- Meet funder requirements; Funders require a data management plan as part of the proposal process.
- Share data; Information in the DMP is the foundation for archiving and sharing data with community.
1.2.4 How to Plan
- As indicated above, engaging your team is a benefit of data management planning. Collaborators involved in the data collection and processing of your research data bring diverse expertise. Therefore, plan in collaboration with these individuals.
- Make sure to plan from the start to avoid confusion, data loss, and increase efficiency. Given DMPs are a requirement of funding agencies, it is nearly always neccesary to plan from the start. However, the same should apply to research that is being undertaken outside of a specific funded proposal.
- Make sure to utilize resources that are available to assist you in helping to write a good DMP. These might include your institutional library or organization data manager, online resources or education materials such as these.
- Use tools available to you; you don’t have to reinvent the wheel.
- Revise your plan as situations change and you potentially adapt/alter your project. Like your research projects, data management plans are not static, they require changes and updates throughout the research project process.
1.2.5 What to include in a DMP
If you are writing a data management plan as part of a solicitation proposal, the funding agency will have guidelines for the information they want to be provided in the plan. A good plan will provide information on the study design; data to be collected; metadata; policies for access, sharing & reuse; long-term storage & data management; and budget.
A note on Metadata: Both basic metadata (such as title and researcher contact information) and comprehensive metadata (such as complete methods of data collection) are critical for accurate interpretation and understanding. The full definitions of variables, especially units, inside each dataset are also critical as they relate to the methods used for creation. Knowing certain blocking or grouping methods, for example, would be necessary to understand studies for proper comparisons and synthesis.
1.2.6 NSF DMP requirements
In the 2014 Proposal Preparation Instructions, Section J ‘Special Information and Supplementary Documentation’ NSF put foward the baseline requirements for a data management plan. In addition, there are specific divison and program requirements that provide additional detail. If you are working on a research project with funding that does not require a data management plan, or are developing a plan for unfunded research, the NSF generic requirements are a good set of guidelines to follow.
Five Sections of the NSF DMP Requirements
1. Products of research
Types of data, samples, physical collections, software, curriculum materials, other materials produced during project
2. Data formats and standards
Standards to be used for data and metadata format and content (for initial data collection, as well as subsequent storageand processing)
3. Policies for access and sharing
Provisions for appropriate protection of privacy, confidentiality, security, intellectual property, or other rights or requirements
4. Policies and provisions for re-use
Including re-distribution and the production of derivatives
5. Archiving of data
Plans for archiving data, samples, research products and for preservation of access
1.2.7 Tools in Support of Creating a DMP

The DMP Tool and DMP Online are both easy to use web based tools that support the development of a DMP. The tools are partnered and share a code base; the DMPTool incorporates templates from US funding agencies and the DMP Online is focussed on EU requirements.
1.2.8 Arctic Data Center Support for DMPs
To support researchers in creating Data Management Plans that fulfils NSF template requirements and provides guidance on how to work with the Arctic Data Center for preservation, we have created an Arctic Data Center template within the DMPTool. This template walks researchers through the questions required by NSF and includes recommendations directly from the Arctic Data Center team.
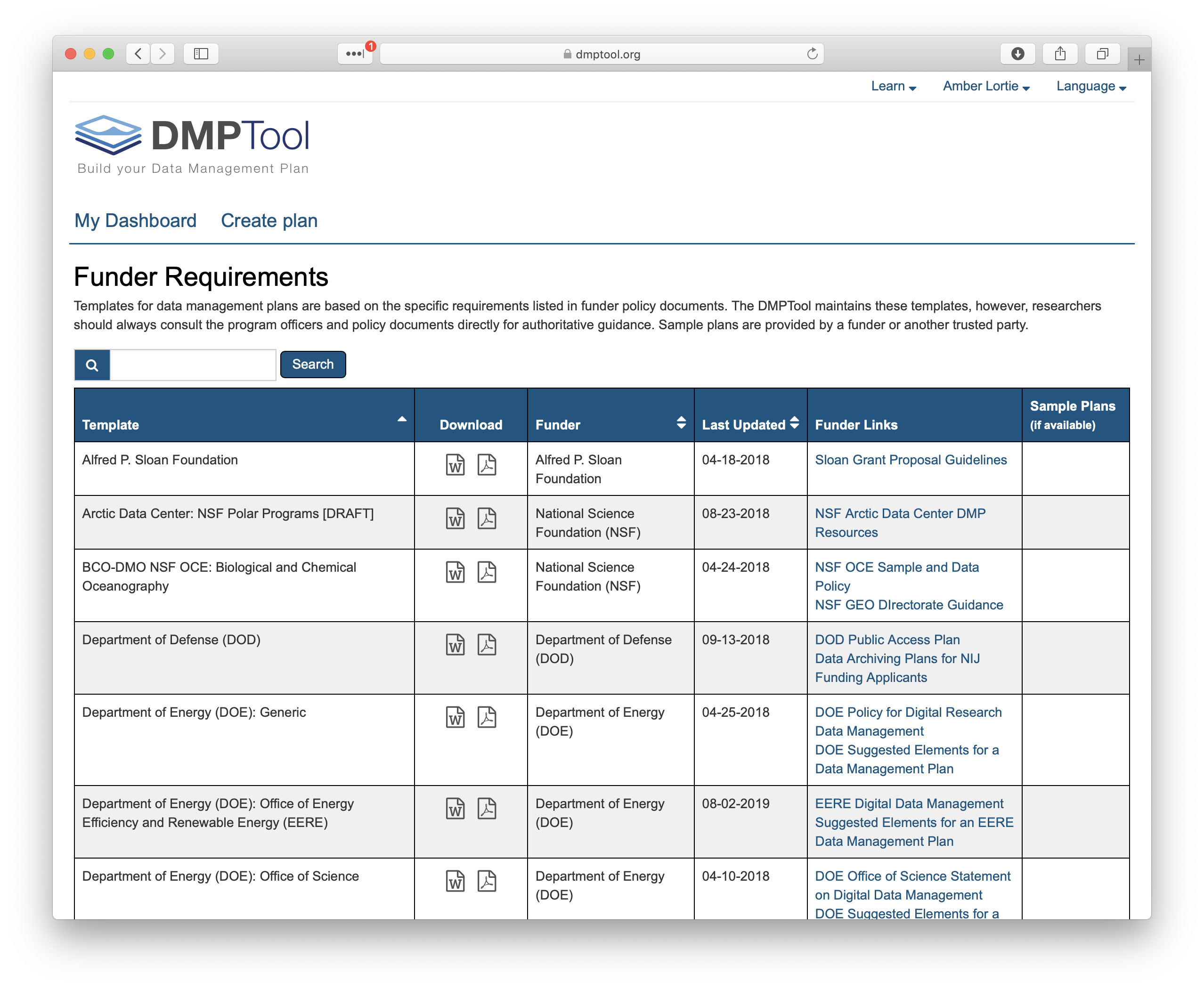
When creating a new plan, indicate that your funding agency is the National Science Foundation and you will then have the option to select a template. Here you can choose the Arctic Data Center.
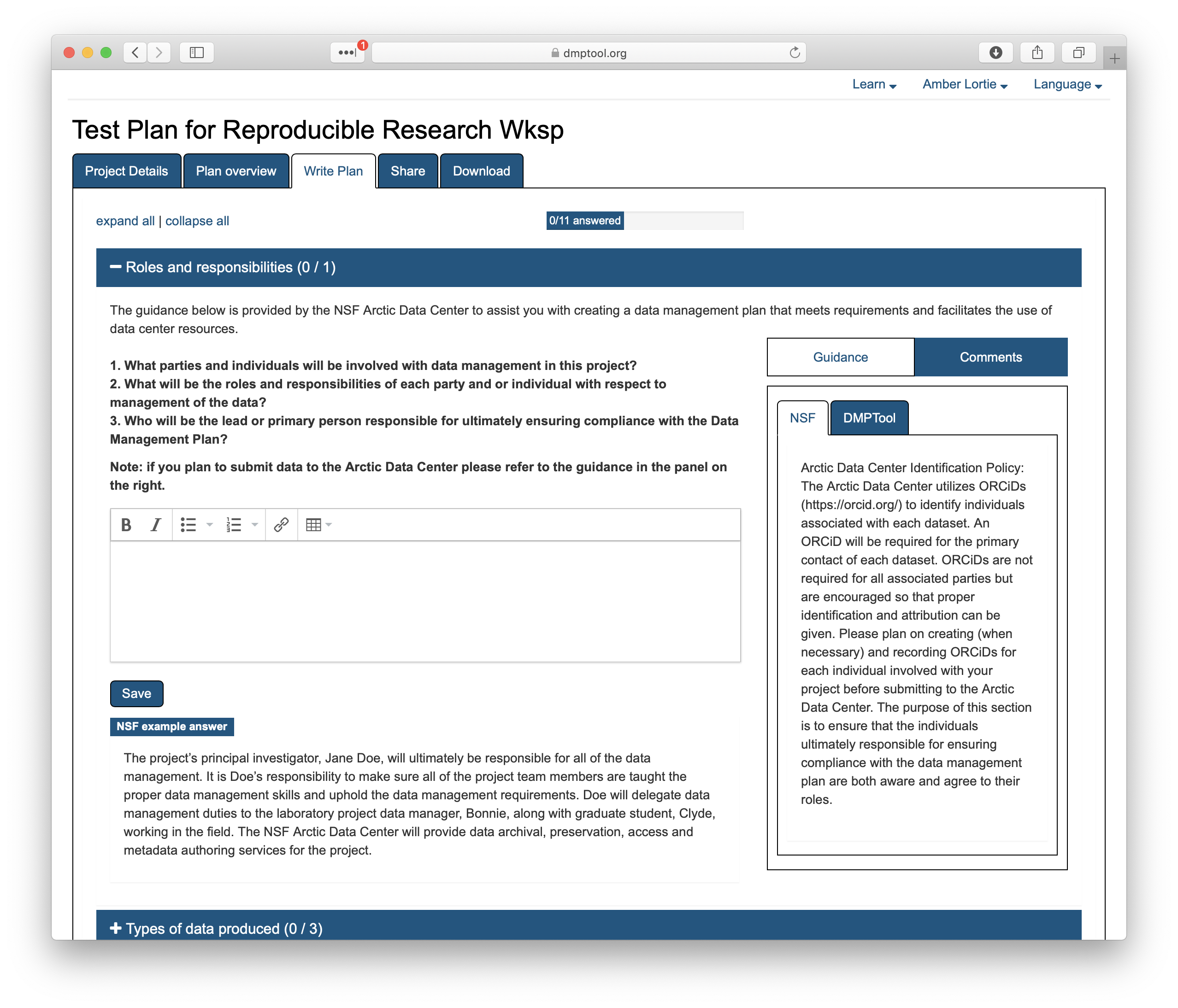
As you answer the questions posed, guidance information from the Arctic Data Center will be visible under the ‘NSF’ tab on the right hand side. An example answer is also provided at the bottom. It is not intended that you copy and paste this verbatim. Rather, this is example prose that you can refer to for answering the question.
1.2.10 Additional Resources
The article Ten Simple Rules for Creating a Good Data Management Plan is a great resource for thinking about writing a data management plan and the information you should include within the plan.